Facial Feminization Surgery


Hairline lowering: techniques
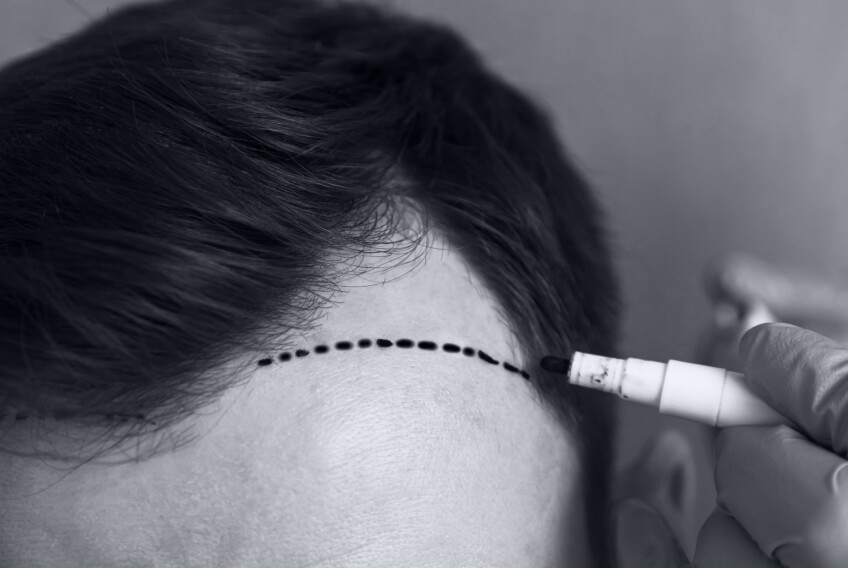
A high hairline or broad forehead can disrupt facial harmony and contribute to self-consciousness. Several medical techniques exist to lower the hairline and achieve a natural, balanced appearance. In this article, we discuss the two main treatment options: hairline lowering through hair transplantation and surgical hairline advancement. We also review combination approaches, differences between male and female hairlines, and what to expect during the recovery process.
1. Hairline Lowering by hair transplantation
A hair transplant is a minimally invasive procedure in which follicles are harvested from the donor area (usually the back of the scalp) and implanted along the new hairline. This method is suitable for:
- Filling receding temples.
- Subtly lowering the hairline.
- Correcting an unnaturally high or poorly defined hairline after previous procedures.
Main hair transplant techniques
a) FUE Technique (Follicular Unit Extraction)
- Individual follicular units (grafts) are removed one by one from the donor area using a micro punch (0.6–1 mm).
- The grafts are then manually implanted into the new hairline.
- Advantages: no linear scar, faster recovery, minimally invasive.
Disadvantages: longer procedure for large graft numbers, donor area must be shaved.
b) DHI Technique (Direct Hair Implantation)
- A Choi implanter pen is used to place follicles directly into the scalp.
- No separate incisions (channels) are required.
- Advantages: higher graft survival rate, quicker recovery.
- Disadvantages: technically more complex, higher cost, less suitable for very large sessions.
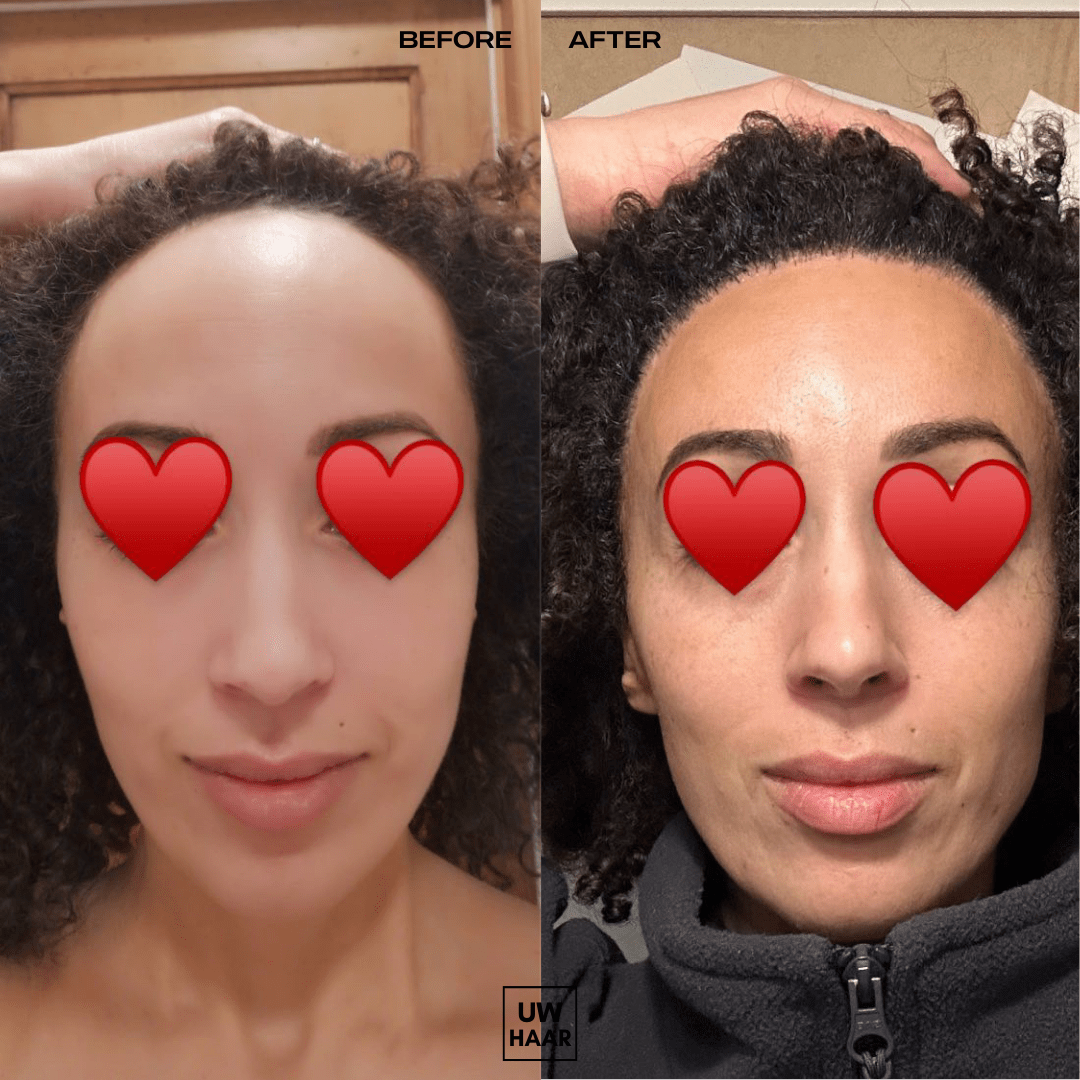
Results and recovery after hair transplantation
- Transplanted hairs often shed in the first weeks (shock loss).
- New growth begins after 3–4 months.
- Noticeable improvement appears at 6–9 months.
Final results are assessed after 12–18 months
More information hair transplantation
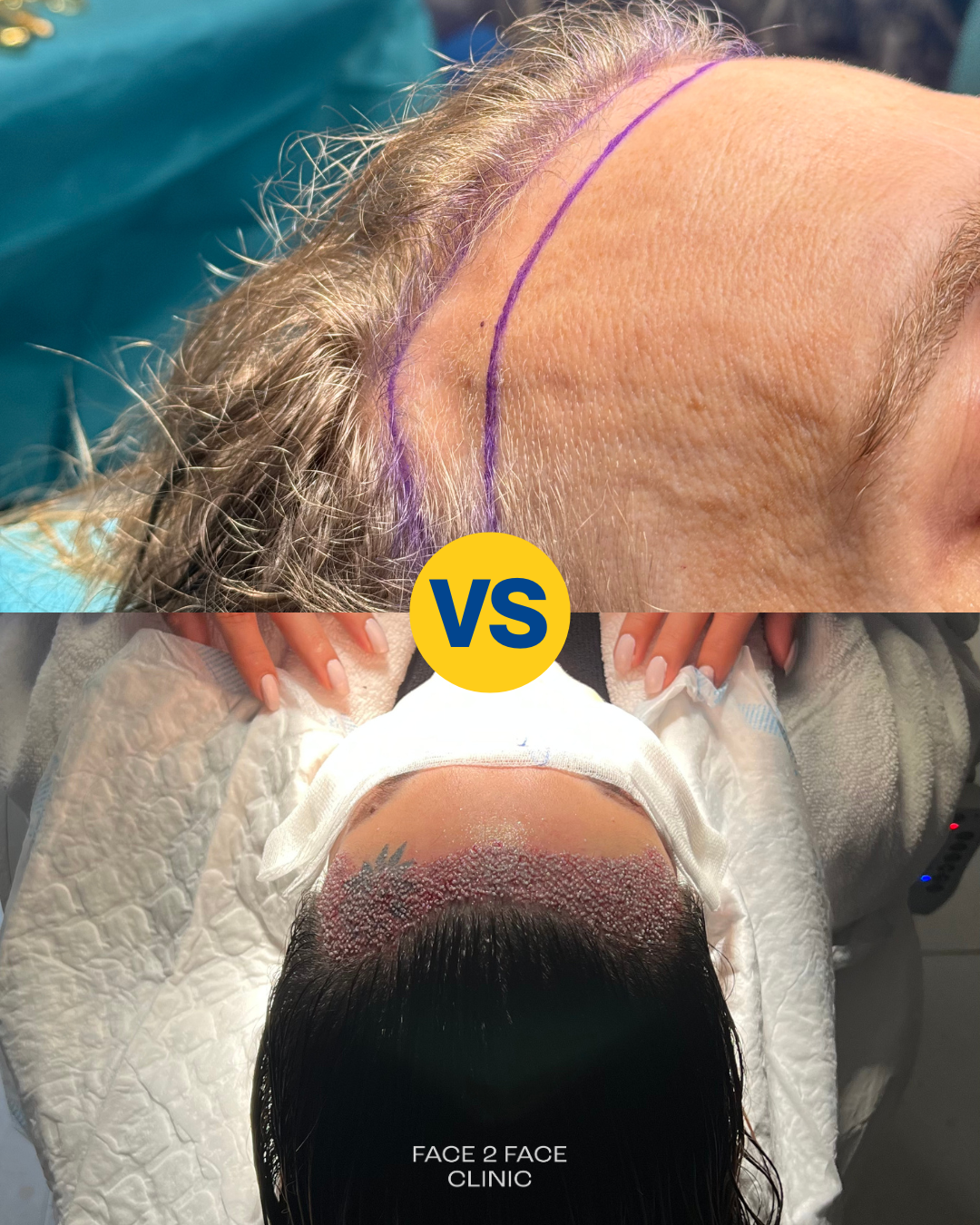
2. Surgical hairline advancement
Surgical hairline advancement is a procedure in which the hairline is moved forward directly by removing a narrow strip of forehead skin.
Procedure
- Under general anesthesia, an incision is made along the hairline.
- A strip of skin is excised.
- The scalp is carefully advanced forward.
- The incision is closed under minimal tension.
- A trichophytic incision technique is often used to allow hair to grow through the scar, improving its concealment.
Possibilities and limitations
- The amount of advancement depends on scalp laxity. On average, the hairline can be lowered 1–3 cm.
- In patients with a tight or inelastic scalp, advancement may be limited.
- The scar is hidden within the hairline and usually fades over time. Postoperative laser therapy (e.g., Fotona laser) is sometimes applied to optimize scar healing.
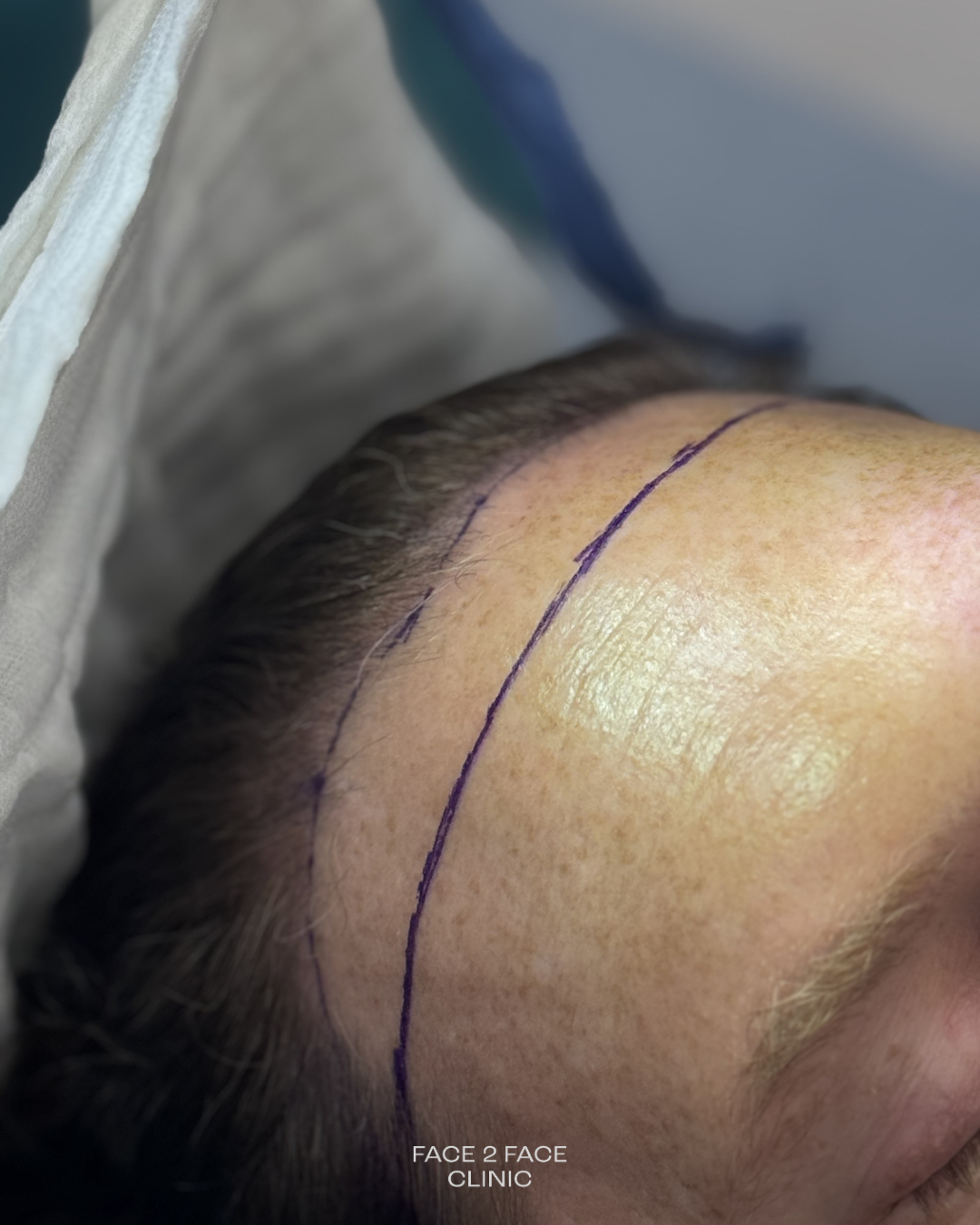
Advantages
- Immediate result.
- Suitable for patients desiring a significant lowering of the hairline.
- Can be combined with forehead contouring and/or brow lift.
Disadvantages
- More invasive than hair transplantation.
- Temporary forehead numbness due to nerve irritation may occur.
More information hairline lowering
3. Combination of surgery and transplantation
In some cases, a combined approach provides the best outcome:
- Surgical advancement moves the hairline forward directly.
- Hair transplantation can then be used to refine the transition and camouflage scars or thin areas.
This dual approach often achieves the most natural and long-lasting results, especially in patients with a very high forehead or low hair density at the front.
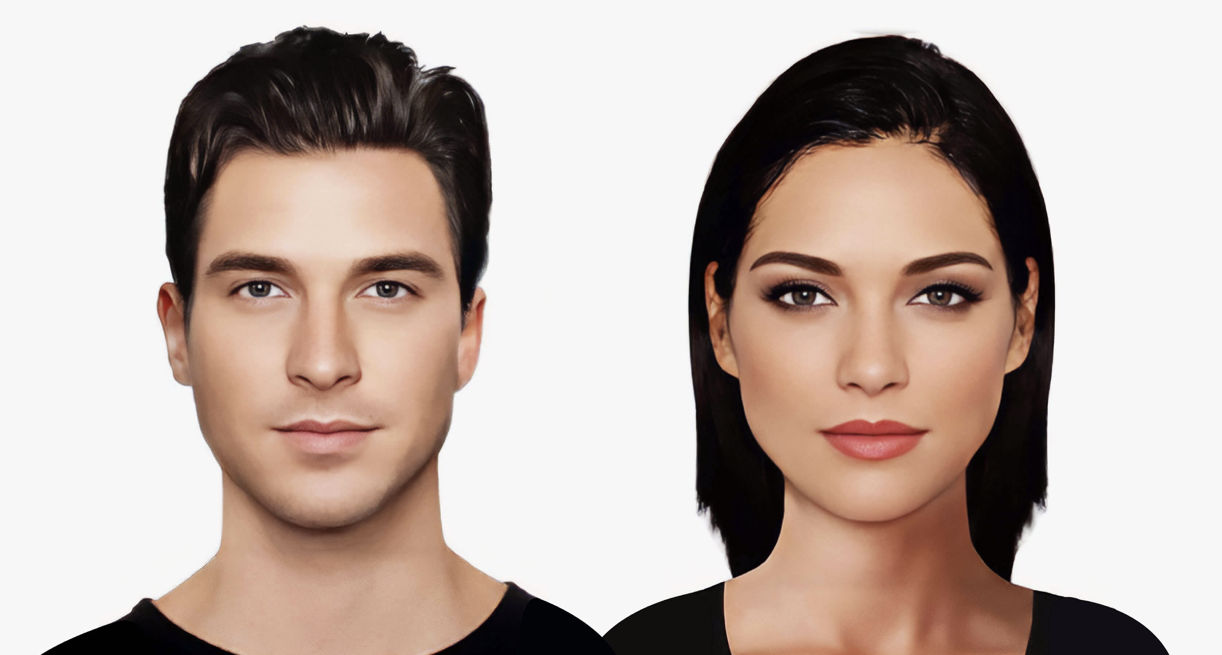
Male and Female Hairlines
Achieving a natural result requires knowledge of anatomical differences:
Female hairline: typically round or inverted U-shaped with minimal temporal recession.
Male hairline: more often M-shaped with deeper temporal recessions.
Gender-affirming surgery: the hairline is reshaped to a more feminine contour.

Factors influencing the hairline
- Hormones: Androgens (such as DHT and testosterone) are the main cause of male-pattern hair loss (androgenetic alopecia).
- Age: Up to 65% of men and 50% of women experience hair thinning with age.
- Medication: Certain drugs (antidepressants, antihypertensives, contraceptives, thyroid medication) may trigger hair loss.
- Lifestyle and care: A balanced diet, stress management, and proper hair care support healthy growth.
Recovery After Hairline Lowering
After hair transplantation
- Shock loss: temporary shedding of transplanted hairs.
- 3–4 months: new hair begins to grow.
- 12–18 months: final result visible.
After surgical hairline advancement
- First weeks: swelling, tenderness, and sometimes temporary numbness of the forehead.
- After 6 weeks: initial hair growth through the scar.
- After 12–18 months: scar typically fades, sensation usually fully recovers, final outcome visible.
Risks and Complications
- Infection (preventable with proper aftercare).
- Scarring (generally well-concealed).
- Temporary numbness.
- Ingrown hairs at the scar site.
Conclusion
Hairline lowering can be performed through different techniques:
- Hair transplantation (FUE or DHI): minimally invasive, gradual results, ideal for detail work and filling temples.
- Surgical hairline advancement: immediate results, suited for significant lowering.
- Combination approach: often the most natural and durable option.
The best choice depends on facial proportions, scalp elasticity, hair density, and patient preference. Most importantly, the procedure should be performed by an experienced specialist who understands both the medical and aesthetic aspects of hairline design.
Contact form
Discover our
combined
treatments
Did you know you can combine your Facial Feminization Surgery with a breast augmentation? Contact us for more information!
Dr. O. Beckers performed my Facial Feminization Surgery (FFS), and I am very happy with the result. Besides the excellent workmanship, I also want to emphasize the accessibility of Dr. Beckers and his team.
Ursula WoutersFacial Feminization Surgery